“It is not what is poured into the student, but what is planted, that counts.” – E.P. Bertin. Teaching vocabulary words and definitions might be troublesome and frustrating for lots of teachers since they think that it is almost impossible for students to understand new terms without memorizing them. What most teachers need to understand, however, is that the issue lies in how the vocabulary lesson is carried out in the first place. One excellent method to properly teach students vocabulary whilst developing their analytical skills simultaneously is the Frayer model. Whether you’ve heard of it before or you haven’t, we’ll explain everything about the model and how to use it in the classroom!
Table of Contents
What is a Frayer model?
At the University of Wisconsin in 1969, Dorothy Frayer and her colleagues wanted to devise a model to help students learn vocabulary and definitions more efficiently. Below is explained the Frayer model definition in great detail:
The Frayer model is a special kind of organizer that allows students to guess and identify the definitions of unfamiliar words that they get exposed to when reading or listening. Often students use the Frayer model before reading a passage to prepare them for words they do not know.
It is also used during the reading process to encourage them to think about vocabulary words. After reading, they take another look at the Frayer model along with the passage to attempt to determine the meanings of words.
This teaching approach aids students’ understanding of new words as they use an analytical strategy to look at these words. This is great for allowing them to think critically as well as independently. The model is not, however, solely based on definitions; it also incorporates examples of the word and some of its characteristics.
Teachers can utilize this method to their advantage; they can easily create numerous activities and games according to the Frayer model to incorporate game-based and peer learning into their day-to-day teachings.
Related article: Including ALL – Why Differentiated Instruction Is Important
Why should you use the Frayer model? – 14 advantages!
Let’s take a look at some Frayer model characteristics that make it the teachers’ favourite teaching strategy in lots of schools around the world.
- Teachers can implement it in almost all grades and subjects
- Students get to engage with the terms given to them, instead of relying on memorization
- The model is quite useful and fun for visual learners
- It helps students actually understand new vocabulary words, with examples and characteristics
- It simplifies evaluation for teachers as it shows them the students’ problem areas
- The model gives students a rich understanding of concepts and definitions, accounting for words with double meanings or words that have layered meanings
- Teachers can implement it for individual students, pairs, or groups
- It requires minimal resources to implementو so it is quite convenient and practical
- The model doesn’t need much preparation or preplanning on the part of the teacher
- Teachers with little classroom experience can easily use it in class whilst getting to understand the students’ levels as a bonus
- The model makes use of students’ background knowledge in understanding new concepts
- It includes further layers of word meanings like examples and comparisons with other concepts/words
- It can encourage students’ social skills as they can discuss findings with one another
- The model consolidates understanding and gives students a comprehensive overview of each word or definition
Students may learn unfamiliar words or concepts using the model and, more significantly, they can absorb those words or concepts so that they become a part of their everyday language. The Frayer Model chart has an oval in the middle for the term or topic being discussed, along with four squares: definition, traits, examples, and non-examples.
This model aims to encourage students to critically think about the word or the topic by describing its characteristics, giving examples and providing non-examples of it.
An article that studied the impact of the Frayer model on improving vocabulary learning concluded that this model demands that students
1) Give definitions for the vocabulary word or concept; and,
2) Employ this data and work with it by thinking of examples and non-examples
How to use the Frayer model to enhance student comprehension?
Choose a word in a reading passage and allow the students to think of the information that they might know in relation to this word. You may suggest examples to help them as a kick-start.
Encourage your class to identify the key elements of the term or idea from the list of examples they have prepared. Help them identify the characteristics and non-examples of the word or idea they generated. A great idea is to record these findings in the four parts, and then go through them.
The next step is to advise the students to read the assignment and look for any extra details that could be included in the four sections on this word or subject. Summarize the material and assist students in defining and giving examples of the term or idea.
After that, divide the students into groups and challenge them to use the strategy to discover the definitions of more terms from a list. At the conclusion of the class, you may combine the findings from the different groups to create an overall template. The class may now exchange ideas, and the teacher can assess the entire class accordingly.
Related article: A Teacher’s Full Guide To Student Behavior Tracking
There are also other techniques to use the Frayer model in the classroom:
1) Guessing the concept/word: Show the students a solved Frayer model with the exception of the word itself. Then, allow the class to attempt a guess according to the hints provided. They can read through the reading comprehension passage if it gets challenging to recognise the word. You can allow them to work on this activity as separate groups so that the group to win would be the one that finishes first.
2) Giving half-empty models: Ask your students to think about what could be missing from their half-empty models. This particular activity could be a great way to refresh their memories if they already have previous information on the topic. It is also an effective strategy to develop their critical thinking skills.
3) Carousel Brainstorming: In this strategy, teachers can distribute templates to each group in the class. They can allow a time frame for each group to fill any chosen box in the model. Afterwards, each group moves on to the next model where the students can add data to the filled boxes. Finally, it would be a great idea for each group to give a brief summary of the final template they worked on.
These techniques can be a great way to encourage the students’ interaction within the classroom when learning new definitions. They are quite easy to use, fun and convenient as well!
Frayer model vocabulary
Now is the time to show you how it’s done! Below is a Frayer model vocabulary example that teachers use to effectively instil vocabulary skills in students in different fields and subjects.
Frayer model diagram
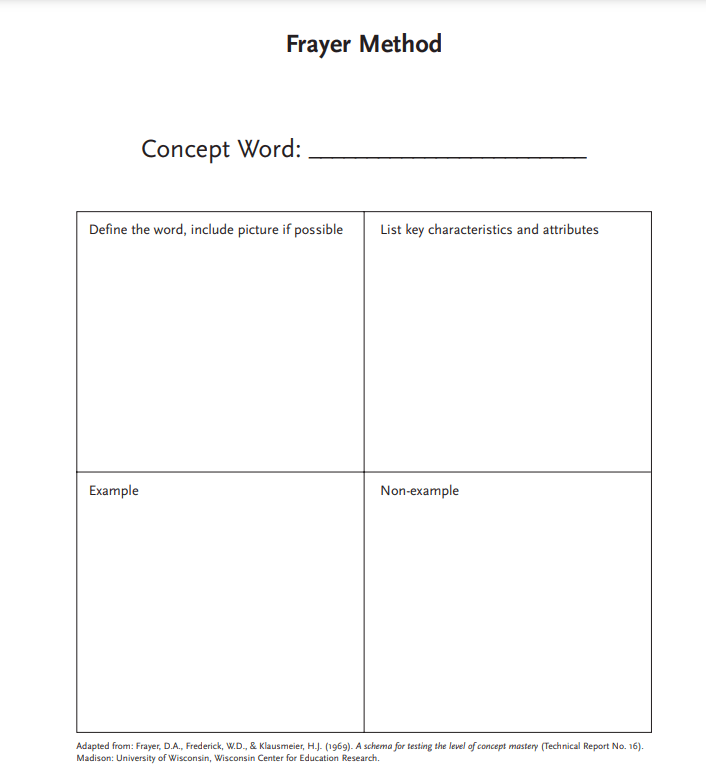
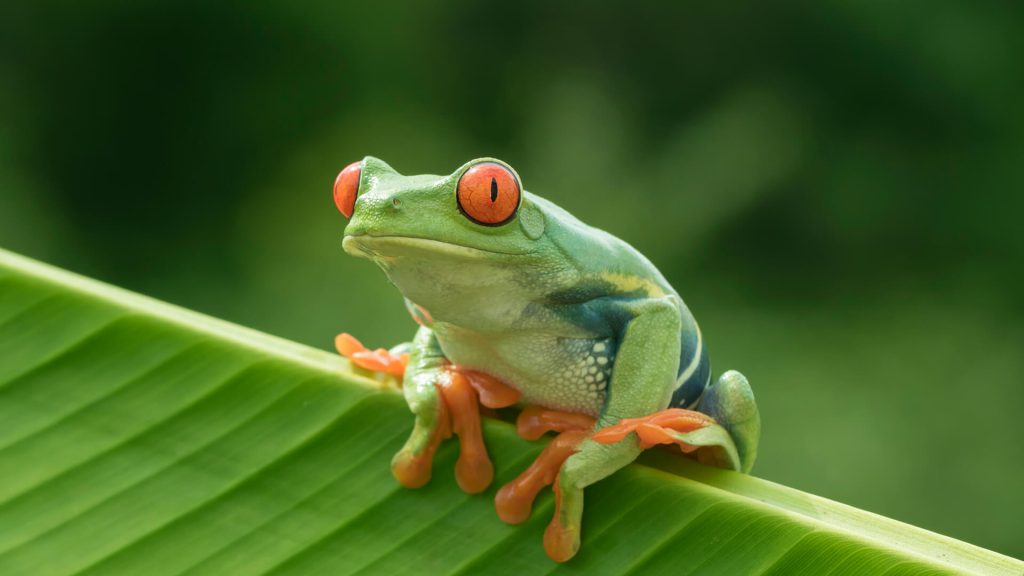
Let’s use the word “amphibian” as an example:
Essential Characteristics
- Cold-blooded
- Breathe through their skin
- Externally fertilize their eggs
- Vertebrates
- Typically have four limbs
- Can live both on land and in water
- Smooth and scale-free skin due to the presence of glands
Examples
- Frogs
- Salamanders
- Toads
- Caecilians

Non-essential Characteristics
- Age
- Gender
Non-examples
- Bears
- Kangaroos
- Dogs
- Elephants
- Insects
Frayer model examples to give you ideas
Here are more examples of the model to use in science and math classes.
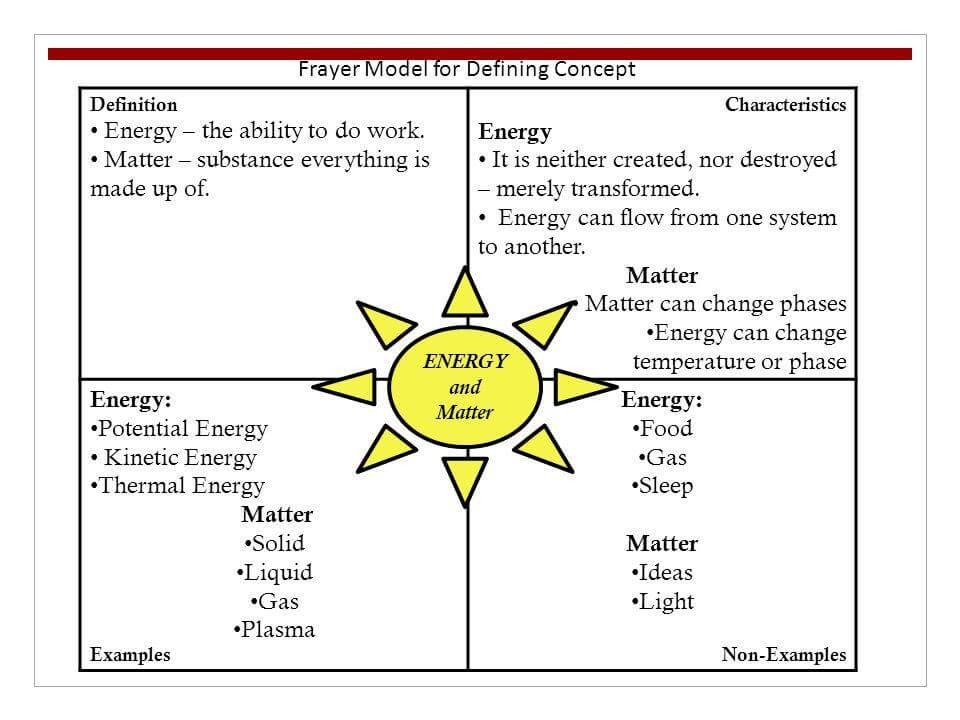
Frayer model science examples
In scientific subjects, there are numerous ways to implement the Frayer model. For example, teachers can:
-Identify the various characteristics of DNA
-Explain animal behaviours
-Discuss different cell types
-Go over different types of chemical reactions and equations
-Define terms like atoms, electrons, molecules and chemical bonds
-Make a classification of living organisms (like mammals, crustaceans, amphibians, etc.)
-Discuss different types of cells (like red blood cells, white blood cells, etc.)
Math Frayer model template
This is one example of a template for mathematics:
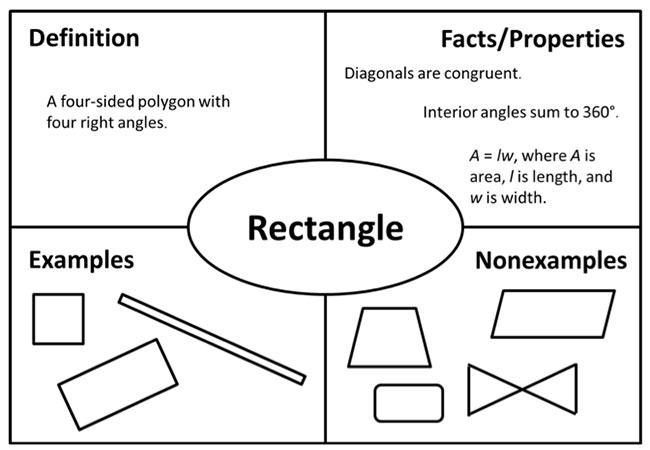
You can also check this pdf that gives examples of using the Frayer model for mathematical concepts and definitions.
This article tackled the significance of Frayer’s model in today’s classrooms and how teachers use it to their advantage when implementing vocabulary skills for their students. We also provided a model for English, Mathematics and Science as well to help teachers grasp its essence and hopefully, use it for their students.
Sources:
1. The Impact of Frayer Model on Improving Preparatory Stage
2. Keys to literacy: Frayer method
3. Biology junction: How to Use Frayer Models in Your Biology Classroom: Five Ideas
4. K12 teacher staff development: How to use the Frayer model to enhance student vocabulary
6. University of Minnesota – K-12 reading strategies Frayer model
 Skolera LMS Blog Educational Technology Articles and News
Skolera LMS Blog Educational Technology Articles and News